Alcohol consumption is a prevalent aspect of social gatherings and celebrations in many cultures worldwide. However, the effects of alcohol on the body can be far-reaching and often overlooked. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the physiological and psychological impacts of alcohol on various organ systems and overall health.
Here are the impacts of alcohol on various organ systems and overall health:
Digestive system
Alcohol's journey through the body begins in the digestive system. Upon ingestion, it is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream through the walls of the stomach and small intestine. This process can lead to irritation and inflammation of the digestive tract, resulting in conditions such as gastritis and ulcers.
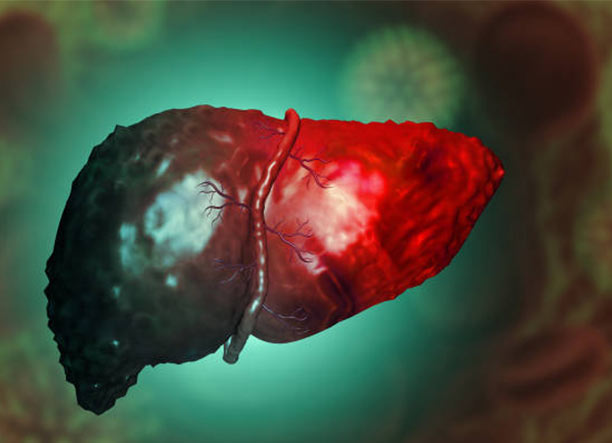
Liver
Liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing alcohol. It breaks down ethanol into less harmful substances, but excessive alcohol consumption can overwhelm the liver, leading to fatty liver disease, hepatitis, and eventually cirrhosis. Long-term alcohol abuse significantly increases the risk of liver cancer.
Brain
Alcohol is a central nervous system depressant, which means it slows down brain function. Initially, it may produce feelings of relaxation and euphoria, but excessive consumption can impair judgment, coordination, and memory. Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to neurological disorders such as Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome and permanent cognitive impairment.
Cardiovascular system
While moderate alcohol consumption has been associated with some cardiovascular benefits, such as increased high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels, excessive drinking can have detrimental effects on the heart and blood vessels. Alcohol abuse is a significant risk factor for hypertension, cardiomyopathy, and stroke.
Immune system
Prolonged alcohol misuse weakens the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Chronic alcoholics are at a higher risk of developing pneumonia, tuberculosis, and other respiratory infections. Additionally, alcohol abuse impairs the body's ability to heal wounds and recover from injuries.
Mental health
Alcohol and mental health are closely intertwined. While some individuals may use alcohol as a coping mechanism for stress or anxiety, excessive consumption can exacerbate mental health issues and increase the risk of depression and suicidal behavior. Alcohol abuse is also linked to an increased likelihood of substance abuse disorders and addiction.
Reproductive health
Alcohol consumption can have profound effects on reproductive health in both men and women. In men, heavy drinking can lead to erectile dysfunction, reduced testosterone levels, and infertility. In women, alcohol abuse can disrupt menstrual cycles, increase the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth, and cause fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) in offspring.
Understanding the effects of alcohol on the body is essential for making informed decisions about alcohol consumption. While moderate drinking may have some potential health benefits, excessive or chronic alcohol abuse can have devastating consequences for physical and mental well-being. By prioritizing moderation and seeking support for alcohol-related issues, individuals can minimize the negative impacts of alcohol on their bodies and lead healthier lives.
Articles
- Celiac disease vs gluten intolerance
- Differences B/W Endoscopy & Colonoscopy
- What is colon cancer or colorectal cancer?
- How Your Gut Health Affects Your Whole Body
- Gas Pain in Chest: Causes, Treatment, and More
- How junk food affects liver health
- The role of probiotics and prebiotics in gut health
- What is indigestion or dyspepsia?
- Why is hydration so important for liver health?
- What are the 5 symptoms of liver disease in women?
- What does alcohol do to your body?
